Back pain is a common condition that affects individuals of all ages. It can range from a dull, constant ache to a sudden, sharp pain and can occur in various regions of the back, such as the lower, middle, or upper spine. Causes of back pain include muscle or ligament strain, poor posture, herniated discs, arthritis, and injuries. In some cases, it results from lifestyle factors like prolonged sitting, lack of exercise, or lifting heavy objects improperly. While most back pain resolves within a few weeks with rest and over-the-counter pain relievers, chronic or severe cases may require medical evaluation, physical therapy, or surgical intervention. Preventive measures include maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and practicing proper posture during daily activities.
Cervical pain commonly known as neck pain, is a condition that affects the cervical spine, which includes the bones, discs, and muscles in the neck. It can result from poor posture, muscle strain, injuries such as whiplash, or degenerative diseases like osteoarthritis. Symptoms often include stiffness, sharp or aching pain, reduced range of motion, and sometimes headaches. In more severe cases, cervical pain can lead to numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arms and hands if nerve compression is involved. Treatment options range from physical therapy, pain relief medications, and lifestyle changes to address posture, to more advanced interventions such as injections or surgery for chronic or severe cases. Early diagnosis and management are crucial for recovery and preventing long-term discomfort.
Disc hernia, also known as a herniated or slipped disc, occurs when the soft, gel-like center of a spinal disc pushes through a tear in the outer layer. This condition typically affects the lower back (lumbar spine) but can also occur in the neck (cervical spine). It often results from wear and tear over time, known as disc degeneration, but can also occur due to injury. Symptoms may include sharp pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs, depending on the disc’s location and the pressure it places on nearby nerves. Treatment options range from physical therapy and pain management to, in severe cases, surgery to relieve the nerve compression and restore function.
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease that primarily affects the cartilage, the protective tissue at the ends of bones. Over time, this cartilage breaks down, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the affected joints. The most commonly affected areas include the knees, hips, hands, and spine. OA is often referred to as "wear-and-tear" arthritis because it tends to develop gradually over time due to aging, repetitive joint movement, or injury. However, other factors such as genetics, obesity, and joint malalignment can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis. While there is no cure, treatments like physical therapy, medication, weight management, and in severe cases, joint replacement surgery, can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for those affected by OA.
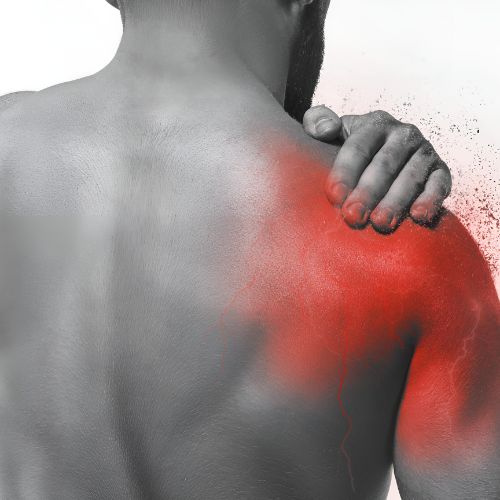
Frozen shoulder, or adhesive capsulitis, is a condition characterized by stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint, resulting from inflammation and thickening of the shoulder capsule. The condition often develops gradually and can significantly limit shoulder mobility, affecting daily activities. Symptoms typically include severe pain, particularly at night, and difficulty in moving the shoulder in various directions. Risk factors include diabetes, previous shoulder injuries, and prolonged immobilization. Treatment options encompass physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and in some cases, corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation.
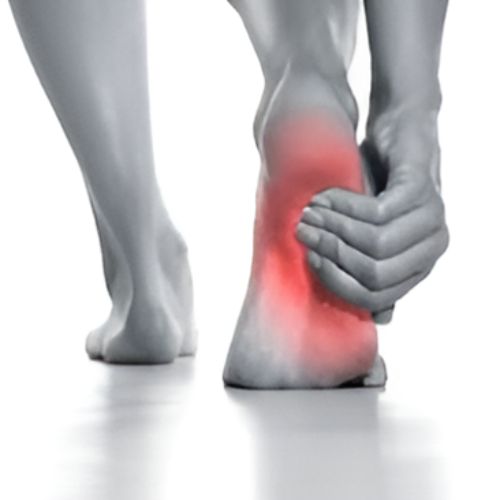
Plantar Fascitis is a common foot condition characterized by inflammation of the plantar fascia, the thick band of tissue connecting the heel to the toes. This condition often causes sharp heel pain, especially with the first steps in the morning or after prolonged periods of sitting. Risk factors include excessive physical activity, obesity, and improper footwear. Treatment typically involves rest, ice therapy, stretching exercises, and the use of orthotic devices to support the arch. In more severe cases, physical therapy or corticosteroid injections may be recommended. Understanding the importance of foot health is crucial, as untreated plantar fascitis can lead to chronic pain and mobility issues.
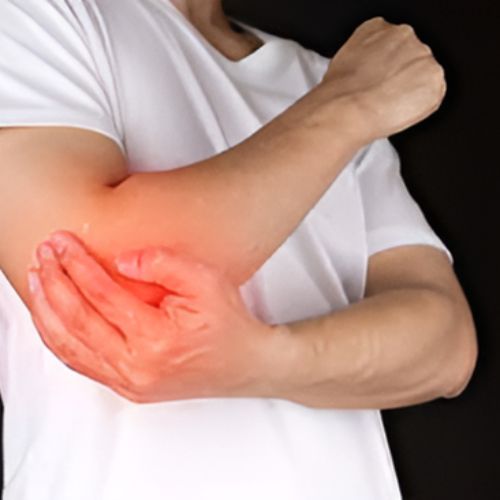
Tennis Elbow, medically known as lateral epicondylitis, is a common condition characterized by pain on the outer part of the elbow. This condition arises from overuse of the forearm muscles, often due to repetitive motions, which leads to inflammation of the tendons that attach to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus. While tennis players are commonly associated with this ailment, it can affect anyone engaged in activities involving repetitive wrist and arm motions, such as painting or playing certain sports. Symptoms typically include pain and tenderness on the outer elbow, weakness in grip strength, and discomfort when performing tasks like lifting or holding objects. Treatment options often include rest, ice application, physical therapy, and, in some cases, corticosteroid injections.
Fractures occur when a bone breaks or cracks, usually due to high-impact trauma, falls, or repetitive stress. They can range from minor hairline fractures to complete breaks that displace the bone. Fractures are classified into several types, including open (compound), where the bone pierces the skin, and closed (simple), where the break remains internal. Other types include comminuted (bone shatters into pieces), transverse (straight across the bone), and greenstick fractures (partial break, more common in children). Symptoms of a fracture include intense pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty moving the affected area. Treatment often involves immobilization with a cast or splint, while severe fractures may require surgical intervention to realign and stabilize the bone using metal plates, screws, or rods.
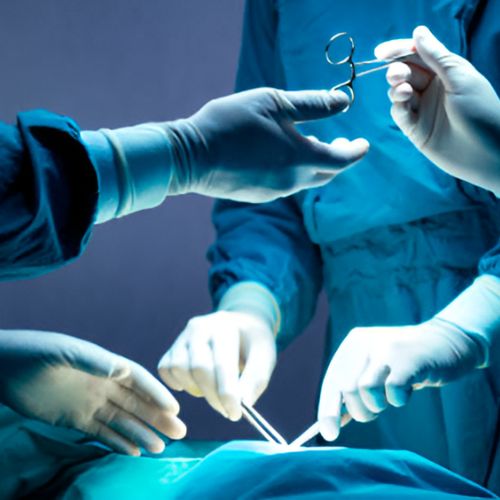
A surgical case involves a medical procedure performed to address diseases, injuries, or other physical conditions that cannot be treated effectively with medication alone. Surgery may be necessary to repair damaged tissues, remove diseased organs, or diagnose internal issues through exploratory techniques. A typical surgical case includes preoperative evaluation, where the patient’s health is assessed, and imaging studies or lab tests are conducted. During the surgery, the surgeon uses specialized tools and techniques to perform the operation, often under anesthesia. Postoperative care is crucial for recovery, involving wound care, pain management, and rehabilitation. Surgical cases range from minor outpatient procedures, such as biopsies, to major operations like joint replacements or heart surgeries, each requiring careful planning and skilled execution by the surgical team.
Ligament surgery, commonly performed for ligament injuries like an ACL tear, involves reconstructing or repairing damaged ligaments to restore joint stability. Ligaments are crucial connective tissues that support and stabilize joints, such as the knee, ankle, or shoulder. In most cases, ligament surgery is required when a ligament is torn or severely damaged due to trauma, sports injuries, or accidents. The procedure often involves grafting tissue—either from the patient’s own body (autograft) or from a donor (allograft)—to replace the damaged ligament. Post-surgery, patients typically undergo rehabilitation to regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion. The success of the surgery and recovery depends on factors such as the injury severity.
Shoulder pain is a common condition that can result from a variety of causes, including injury, overuse, or underlying health issues. The shoulder joint is complex, involving muscles, tendons, and bones, making it susceptible to different types of problems. Common causes of shoulder pain include rotator cuff injuries, tendinitis, bursitis, arthritis, and frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis). Symptoms may range from mild discomfort to severe, limiting pain and restricted movement. Treatments vary based on the cause and may include rest, physical therapy, medications, or in severe cases, surgery. Early diagnosis and intervention are important for effective management and to prevent long-term complications. If shoulder pain persists for more than a few weeks, consulting a healthcare professional is essential.

A strain is an injury to a muscle or tendon (the fibrous tissue that connects muscles to bones), typically caused by overstretching or tearing. Strain often occur in the lower back, hamstrings, or shoulders, and symptoms may include pain, swelling, muscle spasms, and limited movement. A sprain, on the other hand, is an injury to a ligament (the tissue that connects bones to one another), usually resulting from a sudden twist or fall. Sprains are common in the ankles, knees, and wrists, and symptoms may include pain, swelling, bruising, and joint instability. Both injuries require rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) as initial treatments and, depending on severity, may require further medical intervention.
Hip pain is a common condition that can result from a variety of factors, including injury, inflammation, or underlying medical conditions. It often occurs due to issues in the muscles, tendons, ligaments, or joints surrounding the hip. Common causes include arthritis, bursitis, hip fractures, and muscle strains. Osteoarthritis is one of the leading causes of chronic hip pain, particularly in older adults, as the cartilage in the joint wears down over time. Hip pain may also radiate down the leg or into the lower back, making it difficult to walk or engage in everyday activities. Treatments range from physical therapy and medication to more invasive interventions like injections or surgery, depending on the severity of the condition
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition characterized by wide-spread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness in localized areas. It primarily affects the way the brain processes pain signals, amplifying pain sensations. Other common symptoms include sleep disturbances, headaches, memory issues (often called "fibro fog"), and mood disorders like anxiety or depression. The exact cause of fibromyalgia is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. It often coexists with other conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ). Diagnosis can be challenging as symptoms overlap with other conditions, and treatment typically involves a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.