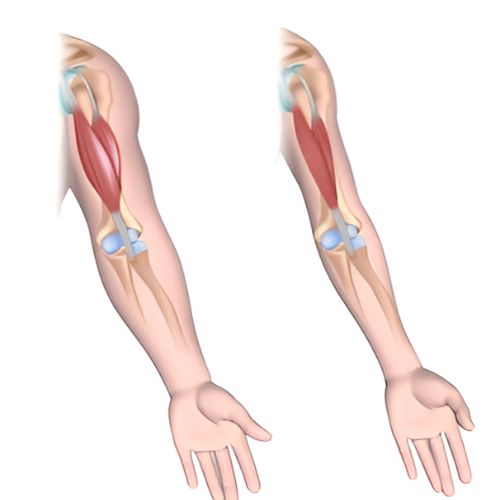
Muscular dystrophy (MD) is a group of genetic disorders characterized by progressive muscle degeneration and weakness. These conditions primarily affect skeletal muscles, leading to challenges in mobility and daily activities. The most common form, Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), primarily affects boys and typically manifests in early childhood. Symptoms often include muscle weakness, difficulty walking, and eventual loss of mobility. Other types of muscular dystrophy, such as Becker, limb-girdle, and mynotonic dystrophy, vary in their onset and severity. Currently, there is no cure for MD, but treatments like physical therapy, corticosteroids and emerging gene therapies aim to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Ongoing research focuses on understanding the genetic causes and developing innovative therapies to slow disease progression.
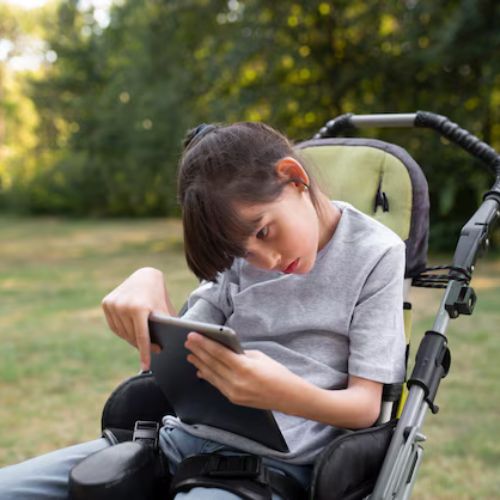

Cerebral Palsy is a group of neurological disorders that affect movement, posture, and muscle tone. It results from damage to the brain during development, often occurring before, during, or shortly after birth. Symptoms vary widely, can include difficulties with coordination, muscle stiffness, and problems with balance. Individuals with CP may experience associated conditions like intellectual disabilities, seizures, and vision or hearing impairments. Therapeutic interventions, such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy, are crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. While there is no cure for CP, early diagnosis and tailored treatment plans can significantly enhance mobility and independence.
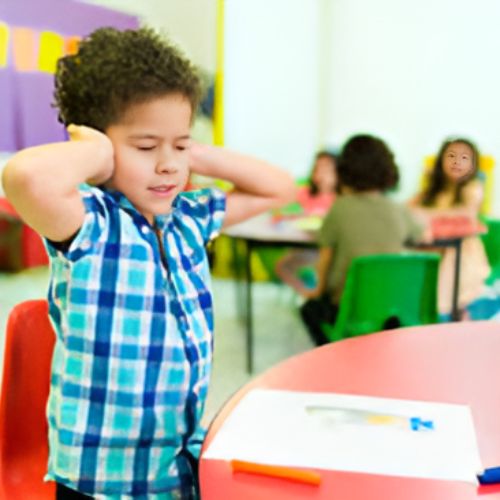

Autism is a complex neuro developmental condition that affects communication, behaviour, and social interactions. It typically manifests in early childhood, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe. Common characteristics include difficulties in social interactions, repetitive behaviours, and restricted interests. While the exact cause remains unknown, genetic and environmental factors are believed to contribute to its development. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes, enabling individuals to develop vital skills and lead fulfilling lives. Treatment may include Behavioural therapies, speech and occupational therapy, and educational support tailored to individual needs. Autism awareness and acceptance are essential to create inclusive environments that support individuals with ASD and their families.